What is an Inverted Yield Curve and Will it Affect You?
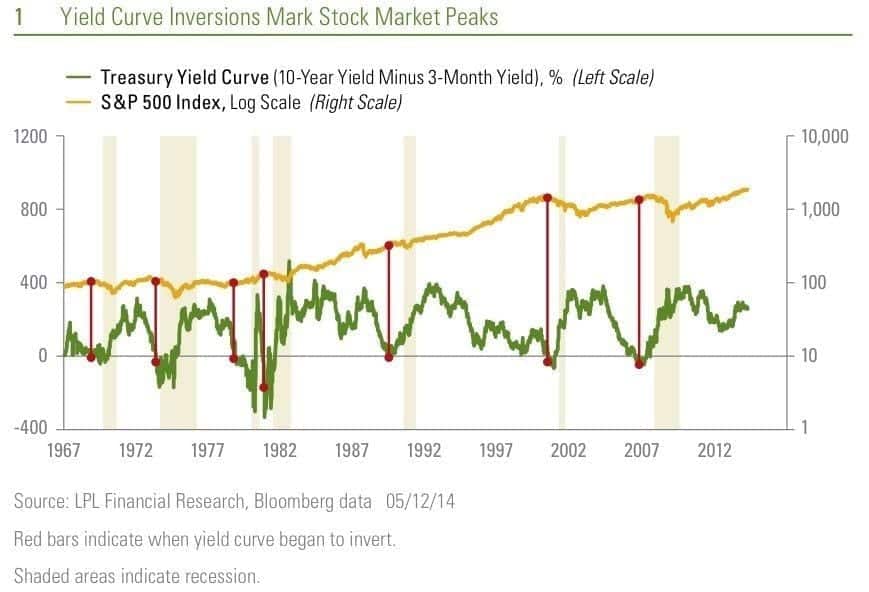
Historically when looking back at past market trends. An inverted yield curve is commonly viewed as an indicator of a pending recession.
In an environment where short-term interest rates exceed long-term rates, market sentiment tends to suggest that the longer-term outlook is poor.
And therefore an economic decline.
Yet predicting when the next recession will actually hit is not so easy. No matter what economists and media pundits may be saying.
Unfortunately economies don’t operate on a set schedule, as much as investors would like them to.
Investor sentiment has a big say in the equation.
So what is an “Inverted Yield Curve”?
An inverted yield curve is often referred to as a negative yield curve.
Once again, when taking a look at previous trends, inversions of the yield curve have preceded the majority of the past US recessions.
Now while history is no guarantee of what will happen in the future, the strong historical correlation is enough for many to put their faith in its accuracy.
With the yield curve often being seen as an accurate forecast of the turning point of a business cycle.
A historical example of this in was back in the year of 2000.
The Treasury yield curve inverted, just before the US equity markets collapsed.
In the below chart we can see this taking place as indicated.
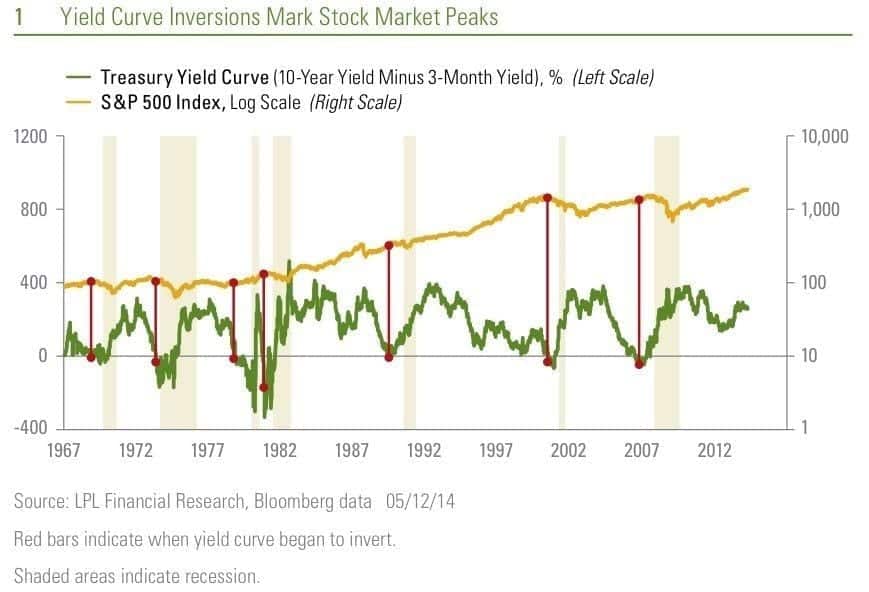
When studying the depth of a yield curve, it’s important to note that it changes in accordance with the state of the economy.
A normal upwards directional curve can be expected when the economy is growing.
And an inverted yield curve is likely to press on when an economy is in a recession.
Fundamentally, this all comes down to a simple relationship between yield curve and economic performance.
So what does this mean for investors?
When an inverted yield curve becomes a trend. It can quickly become an issue for companies that borrow cash on short-term rates.
The same can be said for companies who lend at longer-term rates.
And risk increases in order to generate previous returns.
While it remains open to debate. Whether or not an inverted yield curve is a strong indicator of a pending economic recession. It’s prudent to keep in mind that history is littered with examples of investors blindly following predictions.
A smart investor is one who ignores the noise.
Following trends with a systematic approach is a sure way to improve investment performance over the longer term, which is why I use the Growth Portfolio.
Inverted yield curves don’t last forever.
And when they end, a systematic strategy will adjust accordingly.

